Jul - 23 - 2013
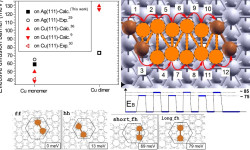
[Phys. Rev. B 82, 085405 (2010)] Understanding materials growth has been a subject of interest already for several decades. The dynamical processes involved in these phenomena in fact bear importance for several aspects of material science; metal oxidation rates and functionality (catalytic, magnetic, etc.) of supported heterogeneous materials when complex structural pattern formation become important, for example. The diffusivity of adatom clusters is long recognized as a critical controlling factor in […]
Jul - 23 - 2013
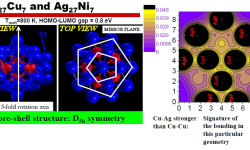
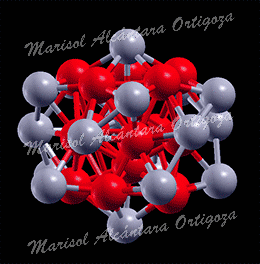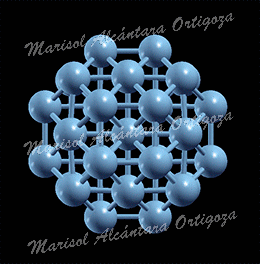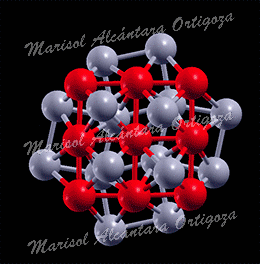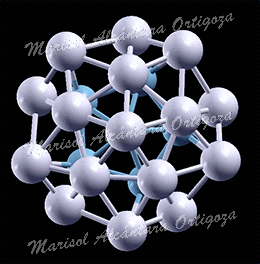
[Phys. Rev. B 77, 195404 (2008) and Contemporary Physics: Proceedings of the International Symposium by Jamil Aslam, Faheem Hussain, Riazuddin; Published by World Scientific (2008)] It is quite clear now that small nanoclusters necessarily have physical and chemical attributes that are distinct from those of their pure bulk counterparts, features that are of course attractive to achieve specific catalytic and optical properties. Needless to say, bimetallic nanoparticles broaden the range of applications, and […]
Jul - 23 - 2013
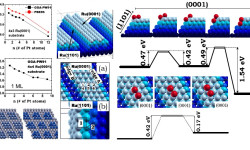
[Phys. Rev. B 78, 195417 (2008) and J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21, 474226 (2009)] This work focuses on understanding the performance of clean energy conversion nanodevices, proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) in particular. Operation of the anode in these devices consists of splitting hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons and Pt atoms on the anode catalyze such process. Unfortunately, the main source of hydrogen is hydrocarbons, which unavoidably contain carbon monoxide (CO) molecules. […]
Jul - 23 - 2013
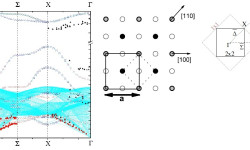
[Phys. Rev. B 81, 115465 (2010)] Controlling and exploiting self-ordering of materials requires us to understand the structure at the atomic level and the mechanism that drives the nanoscale self-assembling. The result of adsorbing nitrogen on the Cu(001) surface constitutes one example of nanoscale self-ordering as it forms squared 6×6 nm2 N-patches on top of the Cu surface. Such structure of N-patches and clean Cu channels is a prototype of templates […]